SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, is a pretty cool lightweight application that runs in your terminal. It is designed to perform secure network operations via a rather insecure network. One of the main features (and the one that I love the most) is being able to login to other systems which run an SSH server. Upon login, the person logged in can access the terminal of the other system. Needless to say, this opens up a ton of sweet tricks that we can use!
Enabling SSH on a Mac is very simple, because SSH is already built into the core of macOS, and can simply be enabled from System Preferences.
Setup Ssh For Mac
On the other computer, open the Terminal app (if it's a Mac) or an SSH client. Type the ssh command, then press Return. The general format of the ssh command is. SSH or 'Secure Shell' is a very useful, secure, and common network protocol for executing command line utilities and transferring files via secure copy, or scp. Follow the instructions in this article to enable SSH for remote management of a Smoke for Mac OS workstation. Aug 16, 2016 If remote login and SSH is currently enabled, the command and report will say 'Remote Login: On' whereas if SSH is disabled and in the default macOS state, it will say 'Remote Login: Off'. Enable SSH on Mac from the Command Line with systemsetup. To quickly turn on SSH server and allow incoming ssh connections to the current Mac, use. May 01, 2019 Mac OS features a built-in SSH client called Terminal which allows you to quickly and easily connect to a server. In this article, we'll outline how to SSH to a server using the Terminal program on OS X Mac. SSH utilizes TCP port 22 by default, although this can be changed to a non-standard port.
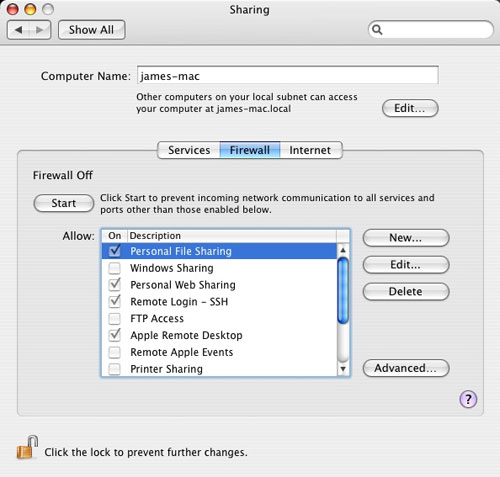
- Open up System Preferences. You can do this by clicking on the Apple logo on the top left corner, and selecting ‘System Preferences…' in the dropdown list.
- Click on ‘Sharing'. As of this writing (macOS Mojave), this icon is the rightmost icon on the 3rd row.
- Tick the ‘Remote login' option on the left side.
That's it! Your Mac is now acting as an SSH server. You can log into your Mac from any other system connected to the same local network as your Mac. Why just the local network? Well, you can expose your SSH server online. Just remember your SSH actually uses a TCP connection underneath and by default runs on port 22. So, this post of mine which details how to expose an HTTP server outside the local network is equally applicable to the case of SSH as well.
Wait, what is the command that I have to give on the other device?
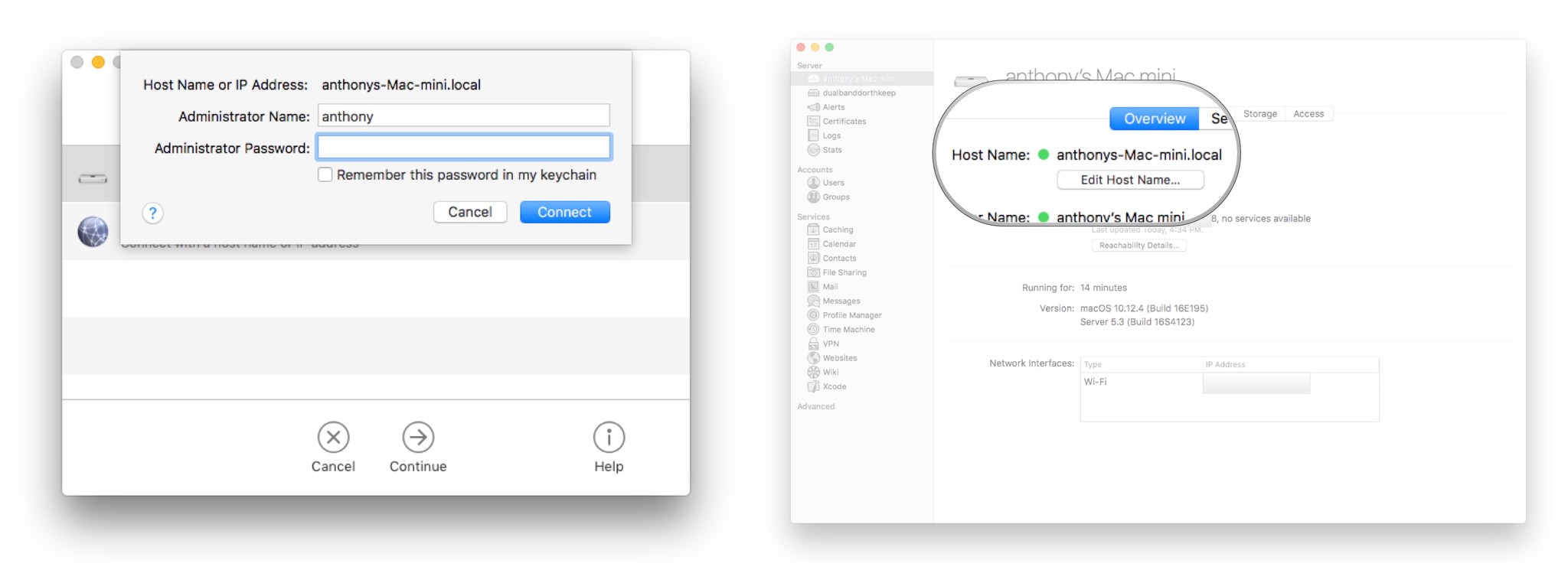
You need to know the local IP address of your Mac. You can easily get this by clicking on the WiFi button on your top right, while pressing your Option key. Alternatively, you may go to System Preferences > Network and get your local IP address listed under Status. Now, the command on the other device is:
For example, if your local IP address is 192.168.1.1 and your username is johndoe, your command is ssh johndoe@192.168.1.1


I'm on a Linux distribution. How do I enable SSH for remote login?
This post is for enabling SSH on a Mac. I will do another post which explains enabling SSH on Linux. As for now, thanks for reading this post and stay tuned for the next one! Peace!
The world is quickly filling up with smarter people who search for smarter ways to work. In this world of smarter brains, working on multiple locations from a single place is a small thing. Many professionals are using remote login protocols to work on multiple machines right from their notebooks. Modern Mac books come with SSH pre-installed but not enabled by default. But you can enable SSH on Mac from the terminal quite easily.
SSH (Secure Shell) is an encrypted remote login protocol used to connect to remote machines over the network. This protocol encrypts communication from an end-to-end server and client machines. SSH protocol is preinstalled by default in all modern Macbooks but the daemon is disabled by default. Mac users can simply enable SSH on Mac using simple terminal commands. You can enable SSH on all versions of macOS and Mac OS X by using the below tutorial.
Check SSH status on Mac
Before we start, let's check the current status of SSH on your Macbook. You can do this by using the system setup command below:
sudo systemsetup -getremotelogin
If the remote login and SSH is currently enabled, the output will say 'Remote Login: On' If SSH is disabled, it will say 'Remote Login: Off'.
How to Enable SSH on Mac from Terminal
- Open the terminal on your Mac.
- You need administration privileges to enable SSH on your Macbook. Use the below system setup command to enable SSH on Mac:
- There won't be any confirmation message for the above command. So, you need to check the SSH status using the 'getremotelogin' command:
- Now you can remote login to another machine using its IP address:
- You need to provide authentication of the user 'technastic' on the machine 'eagle.example.com'
How to Disable SSH on Mac from Terminal
If you feel that you no longer use SSH on your machine, then you can simply turn it off to avoid unauthorized access. You can simply disable SSH on your Mac using the below command:
You'll be asked for confirmation to disable the SSH 'Do you really want to turn remote login off? If you do, you will lose this connection and can only turn it back on locally on the server (yes/no)?' Type 'yes' to confirm.
Enable Ssh For Mac 10.10
SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, is a pretty cool lightweight application that runs in your terminal. It is designed to perform secure network operations via a rather insecure network. One of the main features (and the one that I love the most) is being able to login to other systems which run an SSH server. Upon login, the person logged in can access the terminal of the other system. Needless to say, this opens up a ton of sweet tricks that we can use!
Enabling SSH on a Mac is very simple, because SSH is already built into the core of macOS, and can simply be enabled from System Preferences.
Setup Ssh For Mac
On the other computer, open the Terminal app (if it's a Mac) or an SSH client. Type the ssh command, then press Return. The general format of the ssh command is. SSH or 'Secure Shell' is a very useful, secure, and common network protocol for executing command line utilities and transferring files via secure copy, or scp. Follow the instructions in this article to enable SSH for remote management of a Smoke for Mac OS workstation. Aug 16, 2016 If remote login and SSH is currently enabled, the command and report will say 'Remote Login: On' whereas if SSH is disabled and in the default macOS state, it will say 'Remote Login: Off'. Enable SSH on Mac from the Command Line with systemsetup. To quickly turn on SSH server and allow incoming ssh connections to the current Mac, use. May 01, 2019 Mac OS features a built-in SSH client called Terminal which allows you to quickly and easily connect to a server. In this article, we'll outline how to SSH to a server using the Terminal program on OS X Mac. SSH utilizes TCP port 22 by default, although this can be changed to a non-standard port.
- Open up System Preferences. You can do this by clicking on the Apple logo on the top left corner, and selecting ‘System Preferences…' in the dropdown list.
- Click on ‘Sharing'. As of this writing (macOS Mojave), this icon is the rightmost icon on the 3rd row.
- Tick the ‘Remote login' option on the left side.
That's it! Your Mac is now acting as an SSH server. You can log into your Mac from any other system connected to the same local network as your Mac. Why just the local network? Well, you can expose your SSH server online. Just remember your SSH actually uses a TCP connection underneath and by default runs on port 22. So, this post of mine which details how to expose an HTTP server outside the local network is equally applicable to the case of SSH as well.
Wait, what is the command that I have to give on the other device?
You need to know the local IP address of your Mac. You can easily get this by clicking on the WiFi button on your top right, while pressing your Option key. Alternatively, you may go to System Preferences > Network and get your local IP address listed under Status. Now, the command on the other device is:
For example, if your local IP address is 192.168.1.1 and your username is johndoe, your command is ssh johndoe@192.168.1.1
I'm on a Linux distribution. How do I enable SSH for remote login?
This post is for enabling SSH on a Mac. I will do another post which explains enabling SSH on Linux. As for now, thanks for reading this post and stay tuned for the next one! Peace!
The world is quickly filling up with smarter people who search for smarter ways to work. In this world of smarter brains, working on multiple locations from a single place is a small thing. Many professionals are using remote login protocols to work on multiple machines right from their notebooks. Modern Mac books come with SSH pre-installed but not enabled by default. But you can enable SSH on Mac from the terminal quite easily.
SSH (Secure Shell) is an encrypted remote login protocol used to connect to remote machines over the network. This protocol encrypts communication from an end-to-end server and client machines. SSH protocol is preinstalled by default in all modern Macbooks but the daemon is disabled by default. Mac users can simply enable SSH on Mac using simple terminal commands. You can enable SSH on all versions of macOS and Mac OS X by using the below tutorial.
Check SSH status on Mac
Before we start, let's check the current status of SSH on your Macbook. You can do this by using the system setup command below:
sudo systemsetup -getremotelogin
If the remote login and SSH is currently enabled, the output will say 'Remote Login: On' If SSH is disabled, it will say 'Remote Login: Off'.
How to Enable SSH on Mac from Terminal
- Open the terminal on your Mac.
- You need administration privileges to enable SSH on your Macbook. Use the below system setup command to enable SSH on Mac:
- There won't be any confirmation message for the above command. So, you need to check the SSH status using the 'getremotelogin' command:
- Now you can remote login to another machine using its IP address:
- You need to provide authentication of the user 'technastic' on the machine 'eagle.example.com'
How to Disable SSH on Mac from Terminal
If you feel that you no longer use SSH on your machine, then you can simply turn it off to avoid unauthorized access. You can simply disable SSH on your Mac using the below command:
You'll be asked for confirmation to disable the SSH 'Do you really want to turn remote login off? If you do, you will lose this connection and can only turn it back on locally on the server (yes/no)?' Type 'yes' to confirm.
Enable Ssh For Mac 10.10
Enable Ssh For Mac 10.10
Let us know if you have queries in the comments section below. Do you know about all 3 methods to take a screenshot on your Mac computer? Read our detailed guide.
